

Unlike HDDs, SSDs are less prone to damage due to shock and vibration.
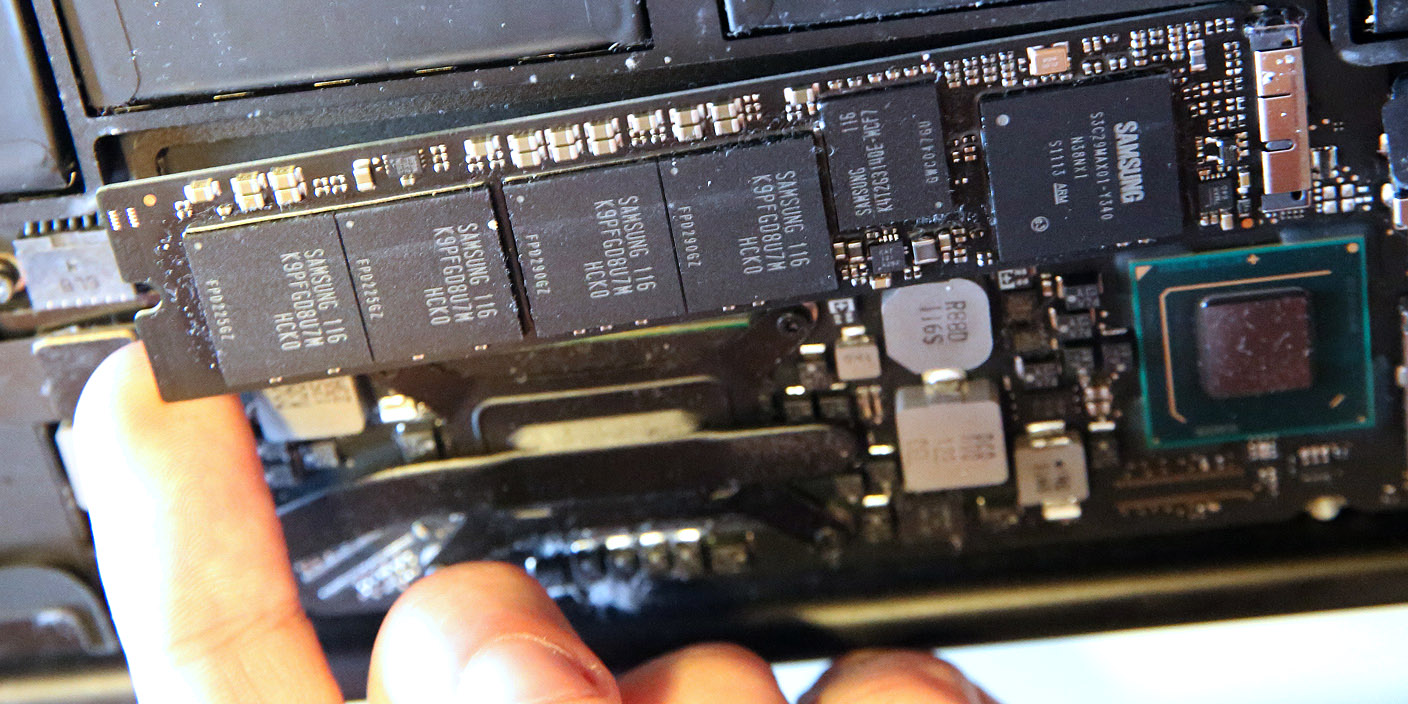
This is not a problem with SSDs, which do not contain parts with magnetic coatings that can be easily damaged by being exposed to a magnetic field. What’s more, HDDs rely on magnetism to write data, so exposing your computer to a strong magnet could erase all information on your drive. And if SSDs fail, your computer would still be able to read data, unless the actual memory chips are damaged.
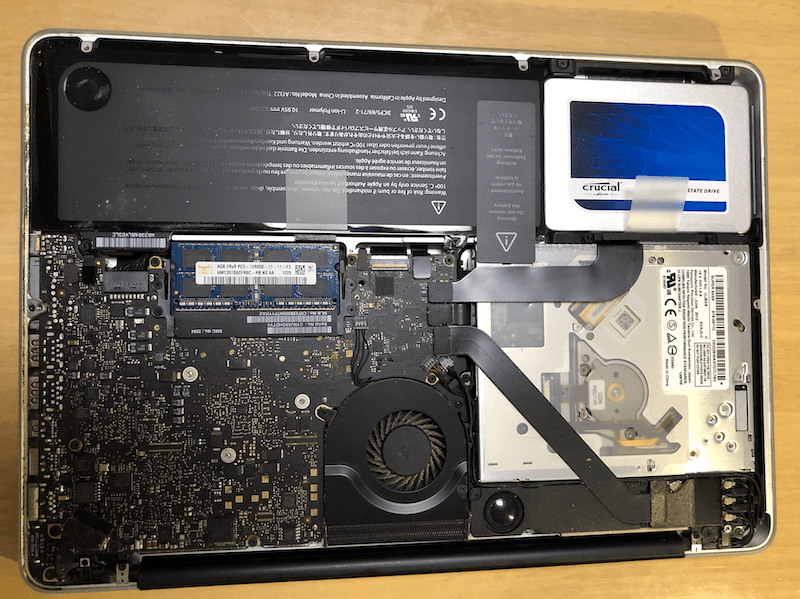
As such, you don’t risk losing or corrupting data in case your SSD is left unplugged. Most consumer SSDs use NAND flash memory, a type of nonvolatile storage technology that doesn’t require power to retain data.
#Ssd for mac mac#
This means your Mac boots up in less than a minute, programs launch and run more quickly, files are transferred faster, and you can do data-intensive work without worrying that your computer will stall or freeze. To access data, a typical SSD takes about 35 to 100 microseconds, which is about 100 times faster than an HDD. SSDs have the clear advantage over HDDs in terms of data access speed. You can enjoy the advantages of SSDs by upgrading your Mac with one today. Newer models, however, have a solid state drive (SSD), which has become the standard in data storage in recent years. If you have an older Mac, it probably has a hard disk drive (HDD) for storing your data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
